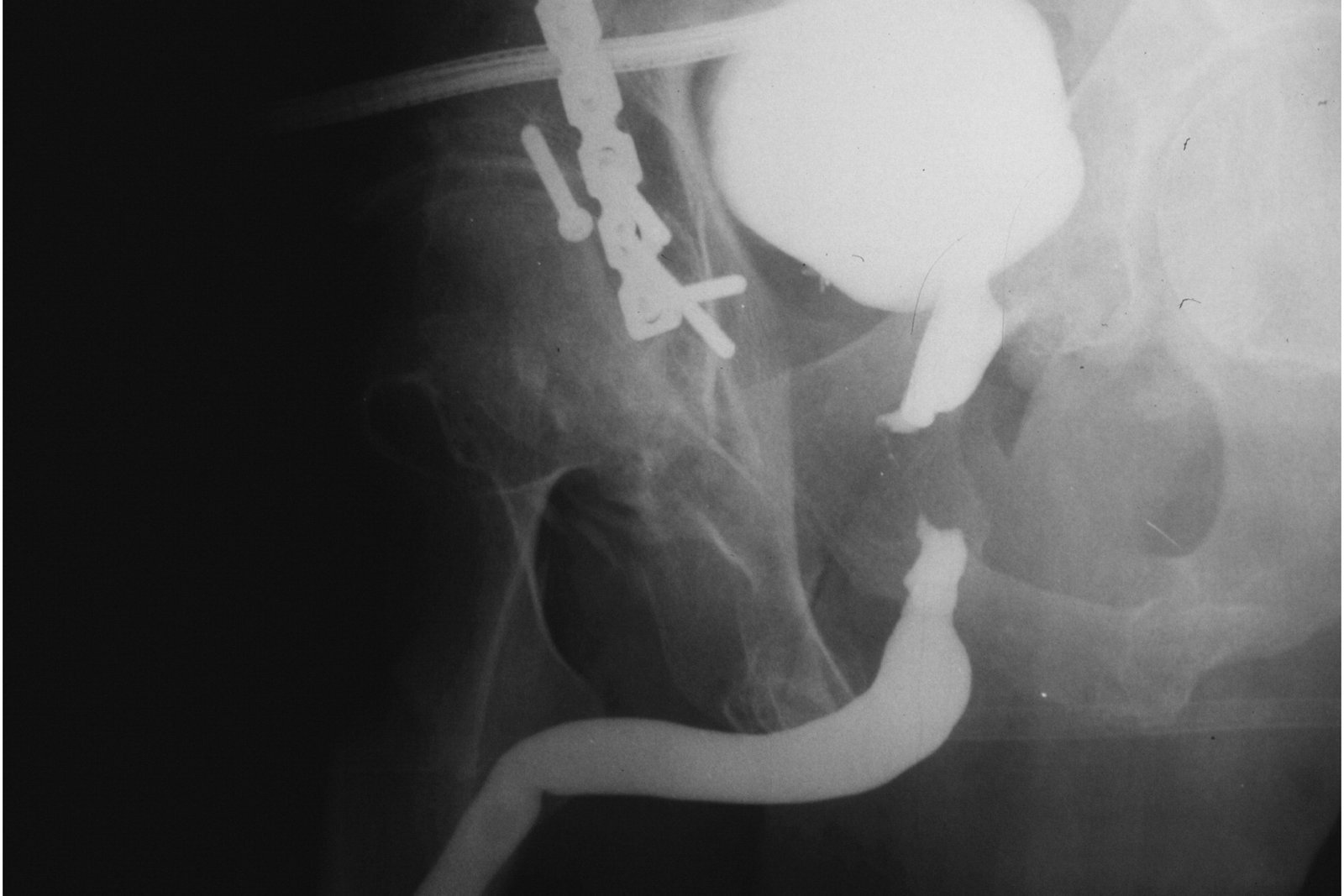
Stricture Dilatation
Stricture dilatation refers to a medical procedure used primarily in gastroenterology to treat strictures, which are narrowed or constricted areas in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. These strictures can occur due to various reasons, such as inflammation, scarring from previous surgeries or injuries, or conditions like Crohn's disease. When a stricture forms, it can obstruct the normal flow of food, liquids, or digestive juices through the affected part of the GI tract, leading to symptoms like difficulty swallowing, pain, or bloating.
The procedure of stricture dilatation involves widening the narrowed area within the GI tract to restore normal function and alleviate symptoms. It is typically performed by gastroenterologists or interventional radiologists using specialized tools called dilators. The dilator is carefully inserted into the narrowed segment of the GI tract, such as the esophagus, stomach, or intestines, under imaging guidance to ensure precision.
There are different techniques for stricture dilatation, including balloon dilatation and bougie dilatation. Balloon dilatation involves using an inflatable balloon attached to the dilator. Once positioned at the stricture site, the balloon is inflated, exerting pressure to stretch and expand the narrowed area. Bougie dilatation, on the other hand, utilizes a cylindrical dilator (bougie) of varying sizes to gently stretch the stricture during the procedure.
The choice of dilatation technique depends on various factors, including the location and severity of the stricture, the patient's overall health, and the preferences and expertise of the healthcare provider. Stricture dilatation is often performed as an outpatient procedure, meaning patients can typically go home on the same day with minimal recovery time.
While stricture dilatation can effectively relieve symptoms and improve the quality of life for patients with GI strictures, it is essential to follow post-procedure instructions provided by healthcare professionals. This may include dietary changes, medications to reduce inflammation or prevent complications, and follow-up appointments to monitor progress and ensure the success of the dilatation procedure in maintaining the patency of the GI tract.
Book Appointment
.jpg)
.jpg)

